Understanding The GSM Network: A Comprehensive Guide
In today's fast-paced world, staying connected is more important than ever. The GSM network, or Global System for Mobile Communications, is a vital component of mobile telecommunications that has transformed how we communicate. With billions of users worldwide, it has become the standard for mobile services, providing a reliable platform for voice and data transmission. This article will delve into the intricacies of the GSM network, exploring its history, functionality, and its role in the modern communication landscape.
The GSM network has played a crucial role in the evolution of mobile technology since its inception in the early 1990s. Originally designed to facilitate mobile voice communications, it has since expanded to include data services, enabling users to access the internet, send texts, and utilize a plethora of applications on their mobile devices. The seamless integration of these services has made GSM the backbone of mobile connectivity in many regions around the globe.
As we navigate through this article, we will uncover the various components that make up the GSM network, as well as the benefits and challenges associated with its widespread adoption. From understanding how it operates to exploring its future prospects, this comprehensive guide aims to provide readers with a clear understanding of the GSM network and its significance in our daily lives.
What is the GSM Network?
The GSM network stands for Global System for Mobile Communications, which is a digital mobile network that is widely used across the globe. It was first developed in Europe and has since become the international standard for mobile communications. The GSM network operates by dividing the coverage area into cells, allowing multiple users to communicate simultaneously without interference.
How Does the GSM Network Work?
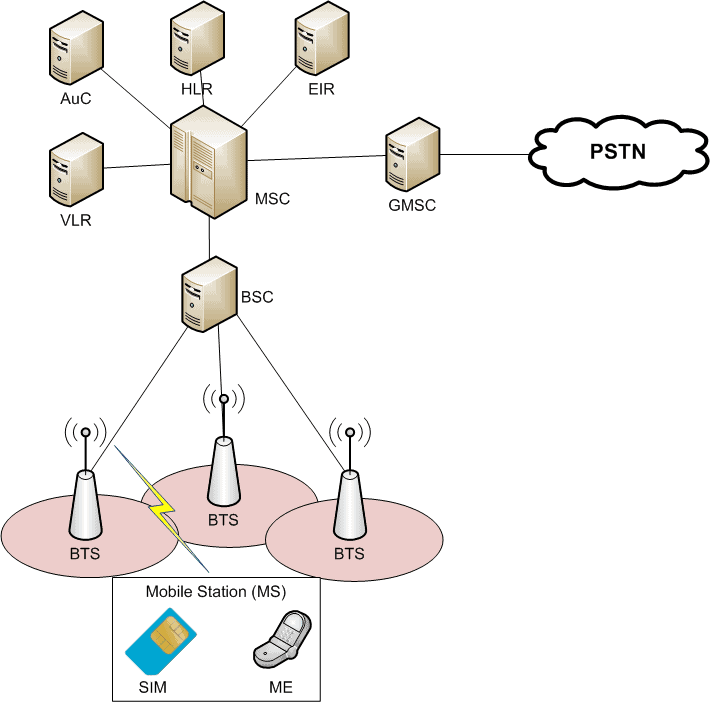
The GSM network functions through a series of interconnected components that work together to enable communication. The main components include:
- Mobile Station (MS): This refers to the mobile device used by the end-user, such as a smartphone or tablet.
- Base Station Subsystem (BSS): This includes the base transceiver station (BTS) and the base station controller (BSC), which manage radio communication with mobile devices.
- Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS): This is responsible for call processing and routing, ensuring that calls are connected to the correct recipients.
- Operation and Support Subsystem (OSS): This component manages network operations and maintenance, ensuring optimal performance.
What Are the Key Features of the GSM Network?
The GSM network boasts several key features that have contributed to its widespread adoption:
- Global Reach: The GSM network is available in over 200 countries, making it one of the most widely used mobile communication systems.
- Interoperability: GSM allows devices from different manufacturers to communicate seamlessly, promoting competition and innovation.
- Security: The GSM network incorporates various security measures, such as encryption and authentication, to protect user data.
- Data Services: Beyond voice calls, the GSM network supports SMS, MMS, and internet services, enhancing the user experience.
What are the Advantages of Using a GSM Network?
The GSM network offers numerous advantages for both users and service providers:
- Reliability: The GSM network is known for its stable and reliable connections, ensuring that users can communicate without interruptions.
- Cost-Effective: The widespread use of GSM technology has driven down costs, making mobile services more affordable for users.
- Scalability: The GSM network can easily accommodate an increasing number of users, making it adaptable to growing populations.
- Enhanced Coverage: The cell-based structure of the GSM network allows for extensive coverage, even in rural areas.
How Has the GSM Network Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the GSM network has been marked by several significant advancements:
- 2G to 3G Transition: The introduction of 3G technology allowed for faster data transmission, paving the way for mobile internet.
- 4G and LTE: The development of 4G networks has further enhanced data speeds and capacity, enabling high-definition video streaming and other data-intensive applications.
- 5G Implementation: The ongoing rollout of 5G networks promises to revolutionize mobile communication with ultra-fast speeds and minimal latency.
What are the Challenges Facing the GSM Network?
Despite its many advantages, the GSM network also faces several challenges:
- Network Congestion: As the number of users increases, the network can become congested, leading to dropped calls and slower data speeds.
- Security Threats: Cybersecurity threats, such as hacking and data breaches, pose significant risks to the integrity of the GSM network.
- Competition from New Technologies: The rise of alternative communication technologies, such as VoIP and newer mobile standards, presents competition for the GSM network.
What is the Future of the GSM Network?
The future of the GSM network looks promising, with continuous advancements in technology and infrastructure. As the demand for mobile connectivity grows, the GSM network is expected to evolve further, incorporating new features and capabilities. Potential developments may include:
- Integration with IoT: The growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) will likely lead to greater integration with GSM networks, enabling connectivity for a wide range of devices.
- Enhanced Security Measures: As cyber threats continue to evolve, the GSM network will need to adopt more robust security protocols.
- Focus on Sustainable Practices: The telecommunications industry is increasingly prioritizing sustainability, and the GSM network will likely adopt eco-friendly practices.
Conclusion: Why is the GSM Network Important?
In conclusion, the GSM network is a cornerstone of modern communication, providing millions of users with reliable mobile services. Its extensive reach, adaptability, and continuous evolution have solidified its place in the telecommunications landscape. As technology advances and user demands grow, the GSM network will continue to play a critical role in connecting people across the globe.
Article Recommendations